What Word Describes the Cooling of Gas by Expansion
Describes the compression or expansion of a gas such that no heat enters or leaves a system. Cooling makes the particles that form the material contract or become tight.
In A Joule Expansion Why Does The Temperature Of An Ideal Gas Remains Constant But The Temperature Of A Real Gas Decreases Quora
Scientists study the behavior of gases extensively.

. The temperature change produced during a JouleThomson expansion is quantified by the JouleThomson coefficient This coefficient may be either positive corresponding to cooling or negative heating. It immediately begins to feel cooler than the others particularly if exposed to some air movement. During the expansion work is done on the surroundings of magnitude where can be taken as the system pressure.
25362 Chemical 17 Nov 03 0654. As it sat around the temperature gradually became the same as the surrounding temperature. The gas heated up when it was compressed.
Thermal expansions of solids liquids and gases. Describe qualitatively the effect of a change of temperature on the volume of a gas at constant pressure. What term describes cooling of a gas by expansion.
Theoretically adiabatic conditions would mean that absolutely no heat could be exchanged between the system the gas and the surrounding environment. What term describes cooling of a gas by expansion. Condensation What describes the initial of clouds of dust and gas.
Gas What describes Uranus. 6 TH TL QH QL W Fundamentals of refrigeration Work W transport of energy only Heat Q transport of energy and entropy 1st law of thermodynamics 2nd law of thermodynamics COP Coefficient Of Performance QQWHL H L H L QQ TT 1 1 LL L HL H L HL QQ T COP WQ Q T T TT Refrigerator. Example of Adiabatic Expansion Assume an adiabatic expansion of helium 3 4 in a gas turbine Brayton cycle.
This makes the gas cold. Just for the sake of exactitude the change in temperature on a isenthalpic-adiabatic drop in pressure a free expansion is called the Joule-Thomson coefficient. Loses internal energy and becomes cooler.
Avail 25 off on study pack. The refrigeration cycle is based on the long known physical principle that a liquid expanding into a gas extracts heat from the surrounding substance or area. Describes what happens to a gas that undergoes an adiabatic compression.
Gases expand the most while solids expand the least. The results of the free expansion can be contrasted against a process of isothermal expansion against a pressure which is slightly different than that of the system as shown in Figure 48. Condensation liquefaction Which word describes the change of substance from gas to liquid.
You can test this principle by simply wetting your finger and holding it up. Identify and explain some of the everyday applications and consequences of thermal expansion. Deluge systems are used to extinguish fires and to dissolve disperse or cool flammable liquids and gases so as to minimize gas expansion andor liquid boil off.
Deluge water also cools structures to prevent deformation or collapse due to heat and can help additional leakage from flanges or connections as well as a vessel rupture. The refrigeration cycle like that used in your freezer is too bulky has too many moving parts to be reliable and does not work well in zero gravity. It is simply the law of energy conservation.
The gas does work on the surrounding atmosphere and so must lose some of its energy since energy is conserved. The mathematical equation for an ideal gas undergoing a reversible ie no entropy generation adiabatic process can be represented by the polytropic process equation where P is pressure V is volume and for this case n γ where C P being the specific heat for constant pressure C V being the specific heat for constant volume γ is the adiabatic index and f is the number of. Fast expansion is an adiabatic process and there is no loss of energy to the surrounding.
The cooling of expanding gasses is usually associated with what is known as an adiabatic expansion expansion in which there is no heat transferred into or out of the gas. In the process of cooling gas exsolves from the lava forming small vesicles. Heating makes the particles that form the material expand or become loose.
One topic of interest is how a gas cools as it expands. There are tow reasons for that cooling on expansion. Table shows some examples of expansion.
This can be accomplished by making the transition happen rapidly or. Condesor- cools the liquid formed gas after compressor compresses. Nebulae Which state of matter best describes the sun.
Word describes a gas changing to a liquid. Railway tracks consist of two. Doing work Lets think of some gas in for example a bicycle pump.
Describe qualitatively the thermal expansion of solids liquids and gases. The regions where each occurs for molecular nitrogen N 2 are shown in the figureNote that most conditions in the figure correspond to N 2 being a supercritical fluid. Cooling is fastest from the surface downward and slower from the bottom of the sheet upward.
Therefore they sometimes use expanding gas to cool the infared cameras. After condensor it pass through the expansion valve then again liquid formed gas expanses to gas form and produses cooling this. Starting early can help you score better.
Therefore the largest vesicles are mostly found in the lower third of the sheet. It would be better to say that gases lose energy when they provide work during expansion. Assume an adiabatic expansion of helium 3 4 in a gas turbineSince helium behaves almost as an ideal gas use the ideal gas law to calculate outlet temperature of the gas T 4realIn this turbines the high-pressure stage receives gas point 3.
To accurately measure this it is best to do it under adiabatic conditions. Gas Expansion Cooling Helium as an example Flynn Ch. Gains internal energy and its temp at increases.
If you pull the. The amount of expansion differs in solids liquids and gases. When gas expands the decrease in pressure causes the molecules to slow down.
Losing energy will imply cooling down. The statement is a relation between energy of the gas and work being done by the gas. The more time available the larger they become.
But if no work is done there could still be a cooling effect for real gases. Adiabatic processes often occur very _. Gas Cooling on Expansion.
If you were to push the pump in quickly then the gas would heat up this is because you are doing work on the gas. Then on expansion the gas cools down.

6 7 Expansion And Contraction Of Materials Particle Model Of Matter Siyavula

Joule Thomson Effect Definition Derivation Formula And Examples

What Are Pv Diagrams Article Khan Academy

Q17 Describe An Experiment To Lido
13 4 Entropy Changes In Reversible Processes Chemistry Libretexts

What Is The First Law Of Thermodynamics Article Khan Academy
The First Law Of Thermodynamics
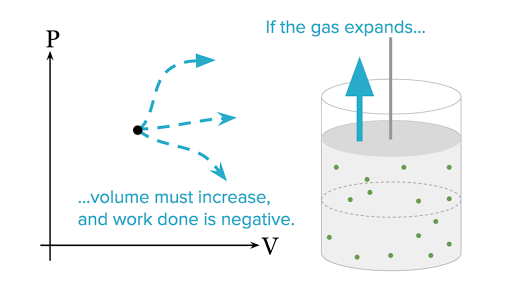
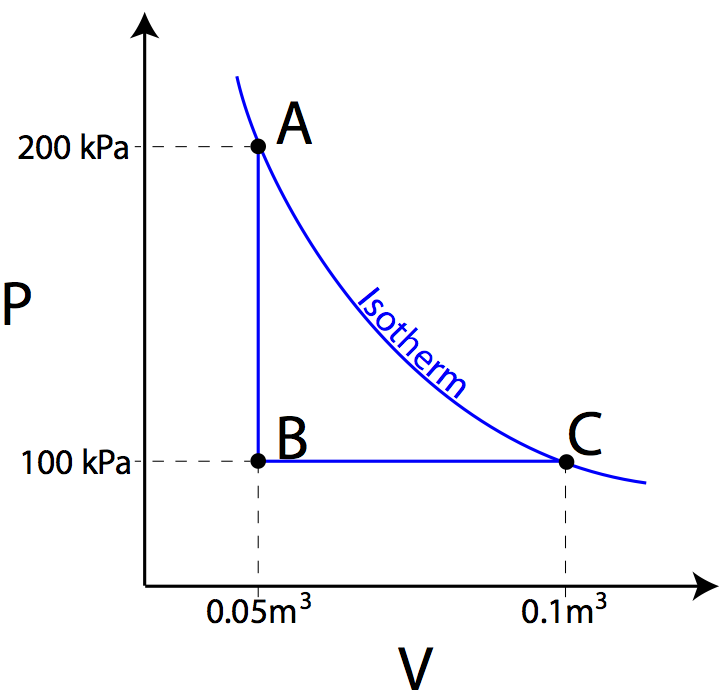
What Are Pv Diagrams Article Khan Academy

Thermal Expansion Physics Britannica

12 2 First Law Of Thermodynamics Thermal Energy And Work Texas Gateway

What Is The First Law Of Thermodynamics Article Khan Academy

Joule Thomson Effect Definition Joule Thomson Coefficient
2 1 Internal Energy Chemistry Libretexts

The First Law Of Thermodynamics And Some Simple Processes Physics

Relating Pressure Volume Amount And Temperature The Ideal Gas Law Chemistry For Majors



Comments
Post a Comment